2023
Authors:
Chen, J., Guo, F., Wu, F., Bryan, B. A.
Abstract:
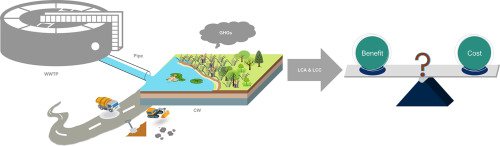
To preserve and restore water ecosystems, China has implemented increasingly stringent emissions standards (Weak, Moderate, and Ambitious) for wastewater treatment plants and constructed wetlands (CWs) are an effective means of improving tailwater standards. We used Life Cycle Assessment and Life Cycle Costing models to quantify the economic and environmental costs and benefits of upgrading drainage standards through CW for 8054 WWTPs in China, and calculated their benefit–cost ratios (BCR). Two land-use scenarios were considered according to whether cultivated land was eligible for use by CWs. The construction phase was the greatest contributor to both environmental impact and cost. BCR were 3.53, 2.49, and 2.39 when cultivated land was ineligible for CW construction and 3.13, 2.16, and 2.20 when eligible. This provides an evidence base for decision-makers to select appropriate emission standards and whether to include cultivated land in the planning of CWs.